使用基于命名的映射来提升命中率
摘要
问题: 多个client向一组服务器请求关于某个对象的服务, 怎么样可以使得这些服务都访问到同一个服务器,以提升命中率?
方法: 本文使用了HRW(Highest Random Weight)的方法, 在客户端使用此方法来解决此问题,以减少响应时间。
简介
背景问题中的CS服务的特点:
- 由一组服务器来响应client端的所有请求,这些服务器是等同的功能和容量/能力;
- 在发送请求之前,client端已拥有了所有服务器的信息。 从client来看,服务端是对等的;
- 服务端有一个 hit rate的说法,主要用来快速响应;例如,服务端是作为cache使用;
- 跨服务器进行对象复制的收益是微乎其微的;
符合上面特点的一些典型域:
- client-side WWW proxy caches
- real-time producer-consumer system
算法name-based mapping的典型描述就是: maps requests to servers such that requests for the same object are sent to the same server, while requests for different objects are split among multiple servers.
对象和服务器之间的 affinities 亲和性 是指 all clients send requests for the same object to the same server. cache affinities的研究显示,将task发送到已经缓存了数据的处理器上,是可以提升cache hit rate.
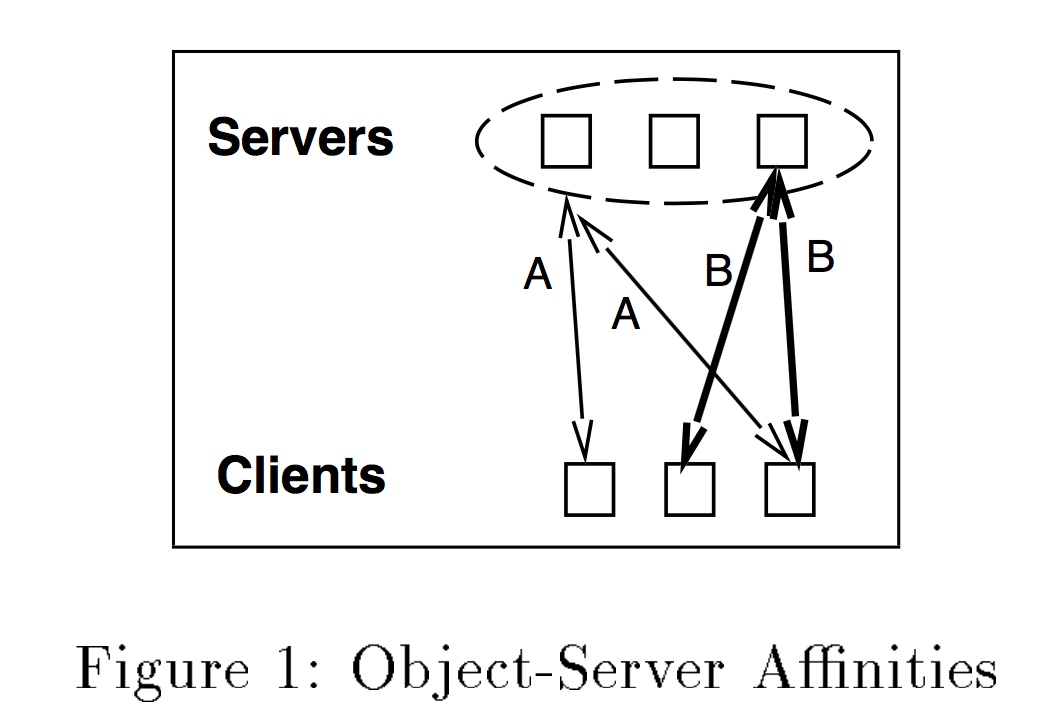
多处理器系统与分布式系统的区别在于:
- 中心化调度与非中心化调度, 分布式系统中cleint对服务端的请求是独立的,非中心化的;
- 延时性,负载信息的及时更新在分布式系统中延时较大;
- request migrate, 在分布式系统中几乎是不可能的,但是在多处理器系统是很常见的;
论文的目标有两个:
- 提升cache hit rates;
- 通过适当调度来减少latency;
本论文的主要贡献:
- mapping requests to servers模型的建立;
- 提出了name-based mapping算法HRW;
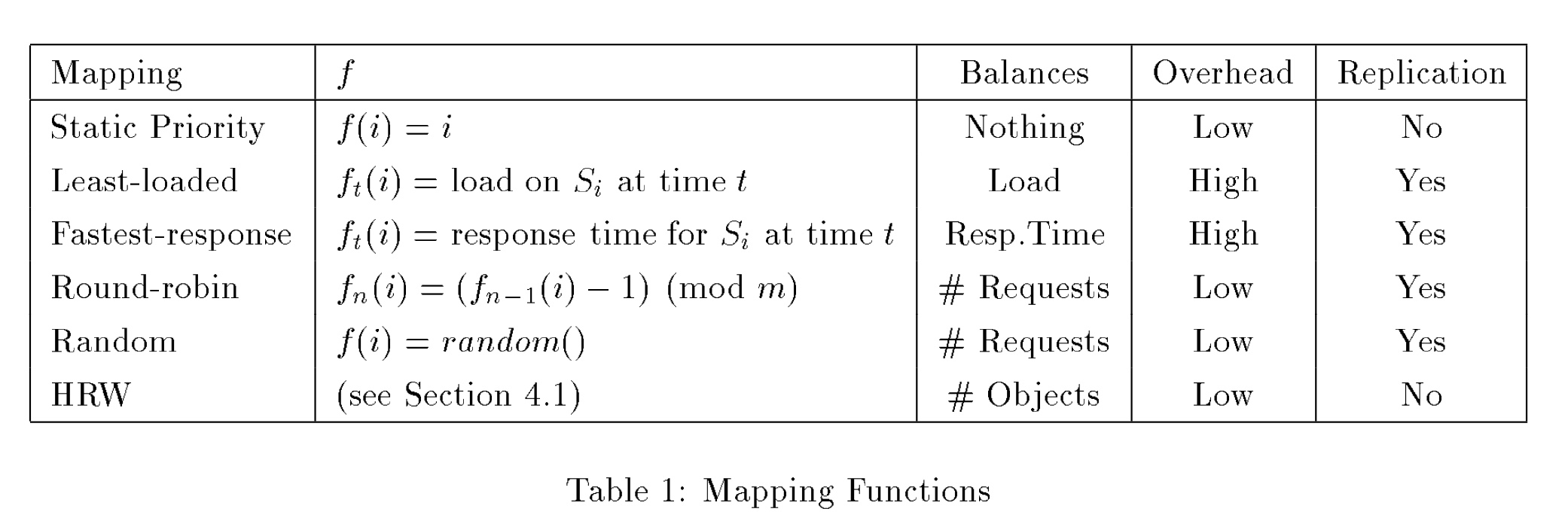
mappings的目标
- load balancing
- “从cluster中选择一个server”引入的延迟必须尽可能地小; local decision VS remote exchange.
- 要保证延迟在各个服务端之间是均匀的,每个服务端应该接收到均匀的、等量的请求, 与对象大小无关,与对象流行度的分布无关;
请求模型主要有:传统的泊松分布; Packet Train, 请求是 in batches/trains到达的(采用这种模型)。 通过公式推导证明两点:coefficient关联系数趋于0时, 服务端之间的负载是平衡的。
- low mapping overhead
- high hit rate, 减少replication,提升命中率;
- minimal disruption. 对象的重分布必须必可能得少。
- disruption coefficient: the fraction of the total number of objects that must be remapped when a server comes up or go down.
- disruption bounds: 1/m <= disruption coefficient <= 1, 其中m是活跃服务端的数目;
mapping requests to servers的模型
本质上就是一个将对对象k的请请r映射到一个服务器Si的函数。
Static Priority Mapping
连接哪个server是静态配置的,例如 f(i)=i。 每个client会尝试着去连接每一个server,直接有响应。可以看出,这种方法具有fault tolerance,但是没有考虑响应时间 以及服务器上cache的利用率问题。
Minimal Load Mapping
当前系统主要使用的方法,client会选择当前最小负载的服务器进行请求。 主要的问题是:
- 需要一个额外的机制来支撑,就是在整个cluster中找出最小负载的哪个机器;这个探测有是代价的,并且要考虑负载检查的及时性问题,因为整个集群内每个机器的负载信息有可能在client知道后已经过时了。
- 在最坏的情况下,有可能所有的client都连接到了某一个服务上,导致很高的负载;
Fastest Response Mapping
选择ping最先响应的那个server来进行请求。 如果地理距离差不多的话,这个算法会退化为load minimal mapping算法。
Round Robin Mapping
最常用的方法就是 f(i) = i (mod m), 通过模算法将请求i映射到m个服务器的某一个上。
Theorem 2: Round Robin Load Balancing. 当request rate高的时候, 这种方法可以达到 Load Balancing。
Randomm Mapping
依据random split理论,随机选择一个server来进行request发送。
Theorem 3: Random Split Load Balancing
mapping based on object names
- 本质上也是一个hash函数, Key是object name, 而bucket是servers。
- 考虑到server可能随时go up, go down,所以hash的结果不可能是一个server,而应该是 a ordered list of servers。
- 这个列表的 ordered则是使用一个打分机制进行排序的。把 object name + server address作为输入, 通过某个函数方法为每一个server计算出一个分数来,然后依据分数的高低来选择server。
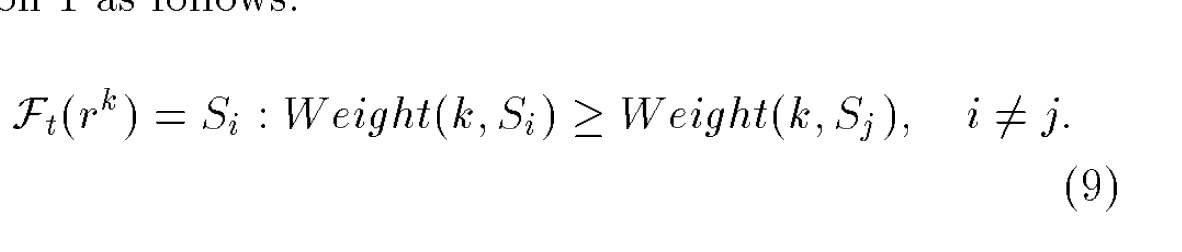
k是对象名字, Si是服务IP地址, Weight是一个打分函数,输入是k和Si.
HRW的属性
low overhead
该算法的输入是object name + server address, 所以可以进行local decision。
当server go down/up的时候, 只需要把所有涉及该down/up server的请求进行 remapping就好。 只要重新为这些请求选择分数最大的server即可。
load balancing
Theorem 4: Hash Allocaton Request Balancing, 说明了随着对象数目的增大, 发送给所有服务器的请求数目将是等同的.
states that the coefficient of variation of qi vanishes as the number of object K becomes large. and qi represents the probability that a request will be sent to Si。
Theorem 5: Hash Allocaton Load Balancing, 说明了当对象数目和请求大小都很大的时候, 每一个服务的处理负载将是均衡的。
states that the amount of processing done by each server is balanced when both K and N are large. let N be request train size the load balancing effectiveness inscreases as the demand increases.
high hit rate
没有replication,可以提高hit rate
mininal disruption
达到了最小下限 1/m
比较
Replication
Theorem 6: Replication growth for random selection
replication会带来一些负面影响,包括: cache space的浪费; 由于cache miss带来的latency较大; full replication的影响会放得更大。
caching
Theorem 7: Partitioning Non Harmful 分区对于缓存是无害的。
under an optimal caching schema, the expected hit rate in a partitioned mappng will be greater than or equal to the expected hit rate in a non-partitioned mapping.
而hash函数的功能就相当于分区的,所以使用HRW会带来hit rate的提升。
Corollary 1: HRW Applicability
HRW is particulary suitable for domains where there are a large number of requestable objects, the request rate is high, and there is a high probability that a requested object will be requested again.
HRW实现
所有client应该使用相同的hash函数。 推荐使用如下函数来计算分数。
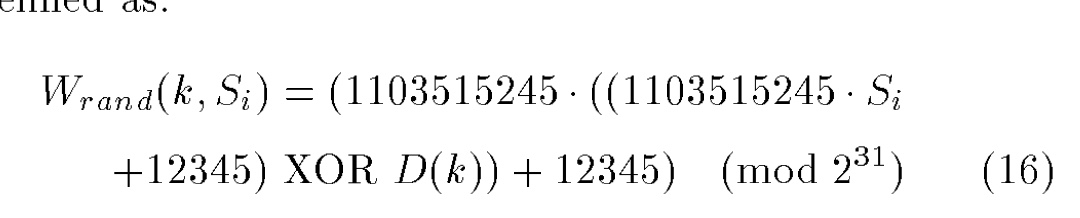
D(k)是依据对象名称k计算得到的digest数值, 而Si是集群中第i个服务的地址。
Theorem 8: 当且仅当 Si == Sj (mod 2^31)时, 函数Wrand中Si和Sj才会有关联。
记分函数的选择和比较
上面给出的记分函数是比较好的。 当然,可能不同的域需要对hash函数进行选择比较。
参考
- using name-base mapping to increase hit rates
- Rendezvous or Highest Random Weight (HRW) hashing algorithm